

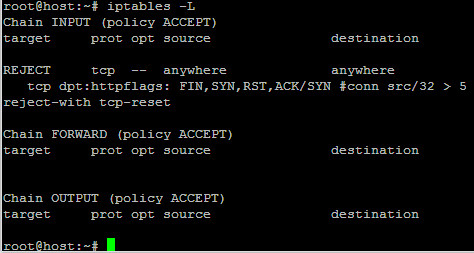

However you may want to only flush all the rules under the INPUT, FORWARD or OUTPUT chain. You can “flush” every rule under iptables by doing: /sbin/iptables -F Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT)įlushing your list of rules can be good if you would like to rewrite your rules completely. Let’s break down what you’re looking at you should see something similar to: (note: the following is an empty table you may have some rules in yours). That will show you your complete iptables rule list, with as much information as possible about each rule. It is also very user friendly, as you’ll soon find out. It supports stateful IPv4, and IPv6 protocol tracking and IPv4 application tracking. Iptables preserves the basic ideas introduced with ipfwadm: lists of rules each of which specified what to match within a packet, and what to do with such a packet. This was merged into Linux 2.3 in 2000, and is still widely used today. This iptables project was begun in 1998 by Rusty Russell. Ipchains also has the ability to filter any IP protocol explicitly, not just TCP, UDP, and ICMP. It supports QoS, Is very flexible with the configuration, as it has “replace” along with “insert” and “remove”. Ipchains which was merged into Linux 2.2.This doesn’t make it the most user friendly linux firewall on the planet. It can filter TCP, UDP, and ICMP packets only. Ipfwadm which was merged into Linux 2.0, which was based on BSD ipfw.There have been 3 main linux firewalls widely used, and they are as follows: Read the first example further down this article. It won’t even know there is a second rule. For instance, if there is a rule to drop all packets coming in through port 21and then a rule directly after that says “accept 192.168.1.*** on port 21” That packet will be dropped once it hits the first rule. As the packet flows through the firewall rules and it reaches a rule that is matches, it stops there and doesn’t continue through the rest of the rule set. In this article, I will either introduce you into iptables for your first time, or help you become more efficient with iptables if you’ve worked with them in the past.Īs network packets flow in and out of the network interface card, they are intercepted, analyzed and manipulated as ruled through the Linux firewall. With the slightest knowledge of Linux firewalls (iptables) you can secure your linux server very quickly and efficiently. Many linux distributions come with several services that you may not use or ever need but they’re running on your server anyways. Modifying rules on your server can cause the server to become inaccessible on port 22 (SSH) or your alternate SSH port.Įveryone in the IT industry is very concerned with security, especially if you’re a linux administrator.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
